Discovery of BMS-986202: A Clinical Tyk2 Inhibitor that Binds to Tyk2 JH2.
Liu, C., Lin, J., Langevine, C., Smith, D., Li, J., Tokarski, J.S., Khan, J., Ruzanov, M., Strnad, J., Zupa-Fernandez, A., Cheng, L., Gillooly, K.M., Shuster, D., Zhang, Y., Thankappan, A., McIntyre, K.W., Chaudhry, C., Elzinga, P.A., Chiney, M., Chimalakonda, A., Lombardo, L.J., Macor, J.E., Carter, P.H., Burke, J.R., Weinstein, D.S.(2021) J Med Chem 64: 677-694
- PubMed: 33370104
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01698
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
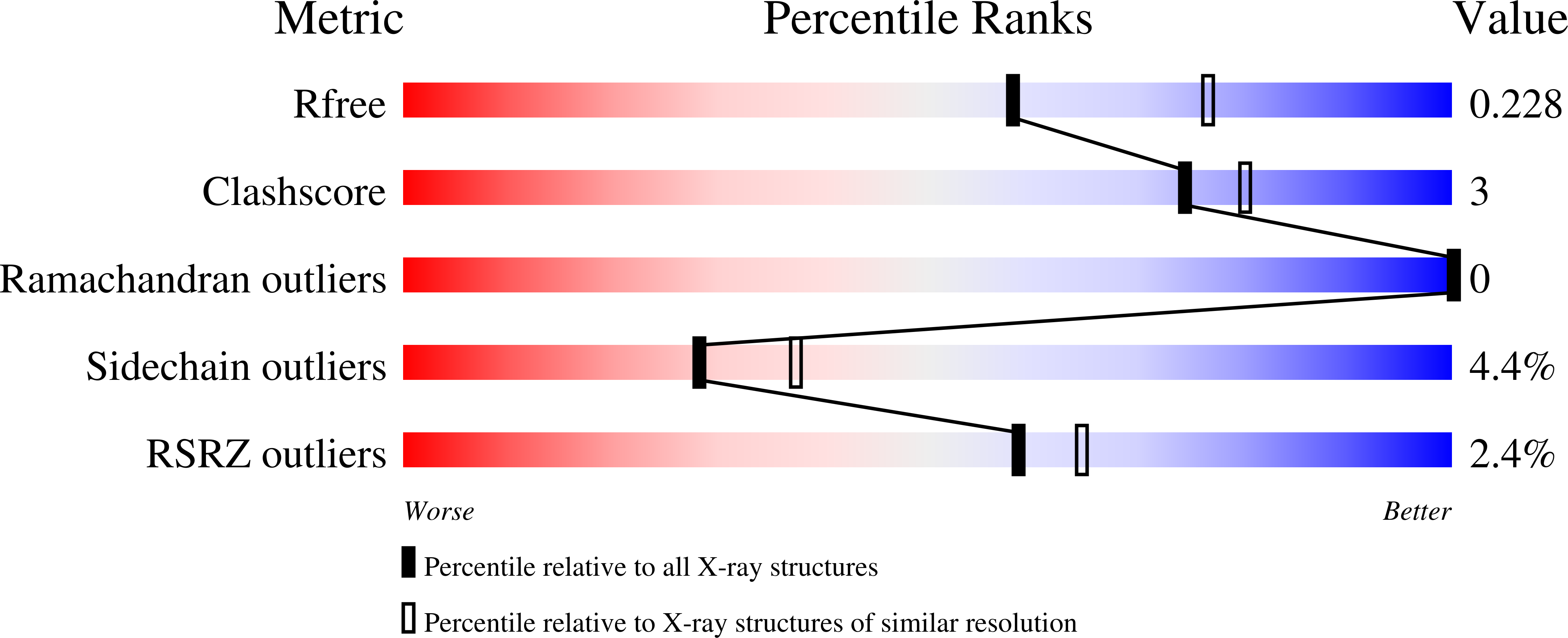
7K7O, 7K7Q - PubMed Abstract:
A search for structurally diversified Tyk2 JH2 ligands from 6 (BMS-986165), a pyridazine carboxamide-derived Tyk2 JH2 ligand as a clinical Tyk2 inhibitor currently in late development for the treatment of psoriasis, began with a survey of six-membered heteroaryl groups in place of the N -methyl triazolyl moiety in 6 . The X-ray co-crystal structure of an early lead ( 12 ) revealed a potential new binding pocket. Exploration of the new pocket resulted in two frontrunners for a clinical candidate. The potential hydrogen bonding interaction with Thr599 in the pocket was achieved with a tertiary amide moiety, confirmed by the X-ray co-crystal structure of 29 . When the diversity search was extended to nicotinamides, a single fluorine atom addition was found to significantly enhance the permeability, which directly led to the discovery of 7 (BMS-986202) as a clinical Tyk2 inhibitor that binds to Tyk2 JH2. The preclinical studies of 7 , including efficacy studies in mouse models of IL-23-driven acanthosis, anti-CD40-induced colitis, and spontaneous lupus, will also be presented.
Organizational Affiliation:
Immunosciences Discovery Chemistry, Bristol-Myers Squibb Research & Development, P.O. Box 4000, Princeton, New Jersey 08543, United States.